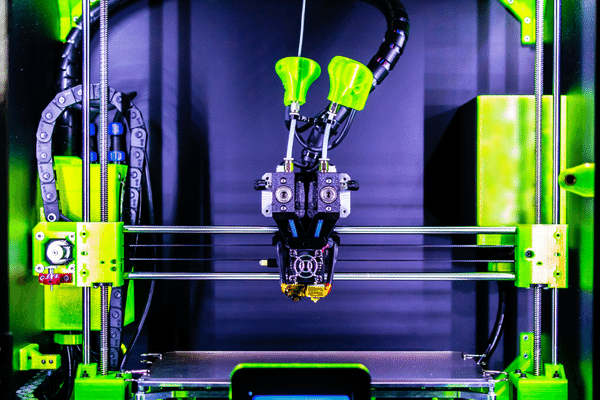
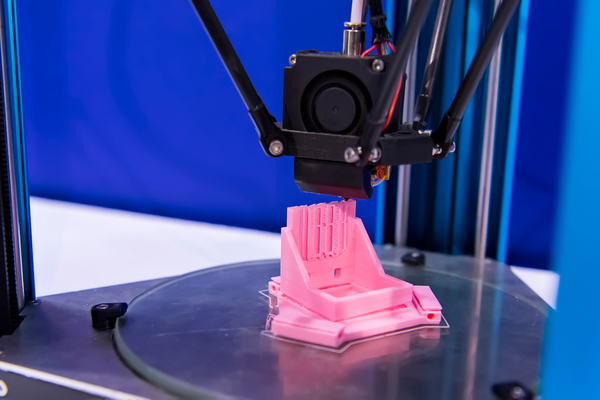
Fused Deposition Modelling (or FDM) printers are a type of additive layer manufacturing (ALM), a form of rapid prototyping technology that allows the safe creation of relatively inexpensive parts. Additive layer manufacturing is one of the fastest growing segments of 3D printing and is changing the way the industry designs and manufactures.
What is FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) 3D printing?
FDM, or fused deposition modeling, is a process of 3D printing that works by extruding heated plastic filament onto a surface. The printer moves along the X, Y, and Z axes to create the desired object.
The first FDM machine was invented by Scott Crump in 1989 and was then known as fused deposition modeling. This technology was first used for rapid prototyping and later became popular in manufacturing industries for its low cost and versatility.
FDM printers are used for various applications, including creating models, prototypes, molds, and even end-use parts.
What are common materials for FDM 3D printing?
The most common materials used in FDM 3D printing are ABS and PLA.
ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene) is a thermoplastic polymer that can be melted and extruded through a nozzle. It’s hard, durable, and has a low coefficient of friction, making it ideal for mechanical parts.
PLA (polylactic acid) is made from cornstarch or sugar cane. It’s biodegradable and doesn’t require special equipment to print with at home. It’s also less brittle than ABS, making it a good candidate for decorative items like toys and figurines.
What are the print parameters for FDM 3D printers?
The following table lists the print parameters for FDM 3D printers.
Extrusion temperature: 235 – 250°C (450-480°F)
Bed temperature: 60 – 65°C (140-149°F)
Printing speed: 30 – 120 mm/s
Layer height: 0.05 – 0.2 mm