Nothing beats the fame and recognition of CNC FCNCmachining and 3D Printing in manufacturing technologies. Both technologies make the job easier for manufacturers, allow more complicated designs, and maximize the overall benefit at little to no additional cost. Does the question remain, which one is the better alternative? CNC vs. 3D Printing is an old debate with no clear answer.

Additive vs. Subtractive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, also known as 3D Printing, creates a three-dimensional object from a digital file. The object is created by laying down successive layers of material until the finished product is formed. Subtractive manufacturing is any process that uses tools to remove materials to create an object.
The goal of additive and subtractive manufacturing is to create the desired product from raw materials. However, in additive manufacturing, these raw materials are typically plastics or metals that are melted and then formed into the desired shape by a computer-guided machine. This process allows for the more precise creation of parts than subtractive manufacturing because there is no waste material left over.
Subtractive processes work by cutting away areas of material until only what remains is what you want. For example, if you want to produce a cube-shaped item using subtractive processes, you start with a block of material and cut away until only three sides remain (the fourth side will be removed later). This process can be time-consuming because it requires multiple steps to produce each part and may require several different tools or machines.
What Is 3D Printing?
3D Printing is a process of making three-dimensional solid objects from a digital file. The process begins with a virtual design sliced into thousands of two-dimensional layers. The printer then builds each layer of the object from the bottom up until it forms the complete 3D object.
The term 3D printing is used to describe several different additive manufacturing processes that can be divided into two categories:
Stereolithography (SLA) uses liquid resin cured with a UV laser to form the model. It’s more expensive than other methods but produces cleaner results with finer details and smoother surfaces. SLA models are often used for precision prototypes and jewelry design.
Polyjet technology uses multiple materials, such as plastics, rubbers, and waxes, to create models with smooth surfaces and high levels of detail. It’s used primarily for industrial purposes such as prototype development and concept models for product design and testing.

What Is CNC Machining?
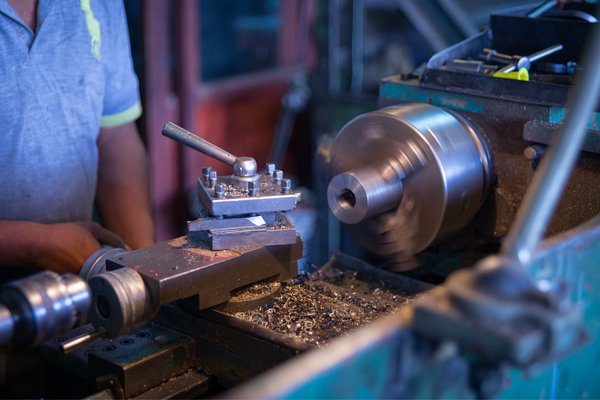
CNC Machining is short for Computer Numerical Control machining. It is a process in which the computer controls the machine tools. The computer uses pre-programmed instructions to control the CNC machine tool, which allows the machine to manufacture products very precisely and accurately.
CNC machining makes metal or plastic parts but can also be used on wood and other substances. The CNC machine tool is controlled by an operator using a CAD/CAM program. The operator loads the material into the CNC machining center, sets up parameters such as cutting speed and feeds per minute, then starts the machine tool. After the program runs, the finished product is removed from the CNC machining center for inspection by quality control personnel before being shipped to customers.
CNC machining centers can be found in many industries, including aerospace engineering, automotive manufacturing, medical devices manufacturing, and electronics manufacturing industries. The use of CNC machining centers has increased dramatically over recent years due to their ability to produce high-quality parts at a faster rate than manual methods such as milling or turning could achieve on their own without any human intervention required during operation other than loading material into the process chamber and removing the finished part from the process chamber. The most common materials used to manufacture parts in CNC machining centers include plastics, metals, and composites.
CNC vs. 3D Printing: 10 Considerations Before Choosing Between the Two
3D Printing and CNC machining have become more accessible and affordable in recent years. The technology is now used in manufacturing, medicine, architecture, aerospace, and many other industries.
Though they both allow you to create 3D objects, they differ in terms of the materials used and the process by which they create them. This article will look at 10 considerations to help you decide between 3D Printing or CNC machining for your project.
The Material
The material is one of the most important factors before choosing a 3D printer or CNC machine. Both machines have advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to know what they are.
CNC machines are typically metal, while most 3D printers use plastic materials. While both machines can be made from other materials, such as wood and ceramic, they often use these materials for their specific designs rather than their main body.
While CNC machines are typically made from metal and other strong materials, the material used in 3D Printing is much weaker than that used in CNC machining. This is because 3D printers use a technique known as photopolymerization that uses light to harden liquid resin into the solid plastic material. This means that if you want something made out of metal, CNC machining may be your best bet.
If you want something made out of plastic or another non-metal substance, then a 3D printer might be more suitable for your needs.

Production Volume
3D Printing is generally used for small-batch production, while CNC machining can handle large runs. If you need to produce many parts or components quickly, CNC machining may be better suited to your needs. However, if you want to produce a small number of parts that require more customization than a single mold can provide, 3D Printing may be the better option for you.
Size of the Part
The size of your part will determine whether you can use CNC or 3D Printing. For small parts, like jewelry or prototypes, 3D Printing might be the better option because it’s faster and cheaper than CNC machining. For larger objects (for example, furniture) or objects with complex geometries, CNC might be the better choice because its accuracy is much greater than what’s possible with a printer.
Design Complexity
CNC machines can handle pretty much any design complexity needed by modern manufacturers. Some companies use CNC machines to make complex parts that would otherwise be impossible with 3D Printing alone. But all that complexity comes at a cost in terms of setup time, material costs, and tooling costs.
If you want to create custom parts for customers who want something unique and highly specific, CNC will likely be your best bet as long as it can handle whatever geometry or materials you need. However, if you’re looking for something more generic or simple in design, then 3D printing may be a better option because it allows for faster turnaround times and lower costs.
Dimensional Accuracy
CNC machining allows you to create complex parts with high accuracy and repeatability. This is a benefit that’s particularly useful when it comes to manufacturing a prototype or working with very small tolerances. And if you need the part to have a specific geometry, such as a hexagonal profile or circular bore, CNC is the way to go.
3D Printing is often used for prototyping because it can be used in place of expensive tooling or casting processes. However, parts produced by additive manufacturing aren’t as dimensionally accurate as those made by CNC machining. They tend to have visible layers and may not fit together seamlessly, even after post-processing with hand tools or other methods.
Surface Finish
3D Printing is best suited for creating prototypes and making functional parts that don’t need a smooth surface finish. CNC machining can handle any other job. CNC machining produces a smoother surface finish than 3D Printing since it uses multiple tools on several axes to remove material from your part. It also allows material removal at an angle, which can be useful for certain jobs like cutting threads or drilling holes with a winding path through the workpiece.

Speed
When comparing the speed of both technologies, you need to consider two factors: material removal rate and toolpath generation time. Material removal rate refers to how quickly the material can be removed from the workpiece using tools such as drills, mills, and lathes. Toolpath generation refers to how long it takes the machine to generate a path for each tool based on the geometry of your part or object.
The material removal rates for both technologies vary widely depending on what type of material you’re working with and what type of tool you’re using to remove that material from your project piece. For example, suppose you’re cutting steel with an end mill or drill bit (a single flute design). In that case, materials such as aluminum (which can be drilled) or plywood (which can be milled) won’t pose much of an issue because they’re soft enough to cut quickly, regardless of the material removal rate. On the other hand, if you’re working with hardened steel (a single flute design), it will take much longer to cut through that material because its hardness makes it more difficult for a tool to remove material from your project piece.
Post-Processing Requirements
In many cases, post-processing is required to complete a 3D-printed part. This can be done manually or with the use of specialized equipment. The amount of time and effort required depends on the material used and the complexity of the design. For example, if you’re printing with PLA filament and need to sand your model down before painting it, you’ll likely spend more time on this step than using ABS plastic.
On the other hand, CNC machining can be done without post-processing work, just as long as your design doesn’t require an intricate finish or intricate shaping. If you want a smoother, more refined surface that feels like glass when touched, CNC machining won’t suffice and will require sanding and polishing afterward (often done by hand).
Eco-Friendliness
3D Printing is a form of manufacturing that creates objects from plastic or metal powders, liquid resins, or other materials fused layer by layer to create an object. The process usually involves a computer-controlled machine that melts and cools the material to create the desired shape. This manufacturing method does not have much waste compared with other types of manufacturing, such as CNC milling, which requires cutting away large chunks of material at once. However, 3D printers can use a lot of energy and resources due to their high power requirements and frequent consumable supplies like plastic filament or metal wire feedstock used for operations like melting and fusing.

Manufacturing Budget
CNC milling might be a better option if you have a limited manufacturing budget. 3D Printing can be expensive and requires a lot of material to produce high-quality parts at a reasonable price. On the other hand, CNC milling involves cutting and fabricating parts out of metal or plastic and does not require much material or time.
Similarities Between 3D Printing and CNC Machining
One common feature of 3D Printing and CNC machining is that they both use a computer-aided process to produce an object. This means that both processes can be highly automated and controlled by software. Both methods allow it to control almost every aspect of the manufacturing process, including tooling and material properties.
Another similarity between 3D Printing and CNC machining is that they’re both subtractive processes — meaning that they remove material from a larger block or form (subtraction) to create an object with a desired shape or geometry. This differs from additive processes like injection molding or casting, where a solid material is added to create an object with a desired shape or geometry.
One advantage of 3D Printing over CNC machining is its flexibility in creating complex geometries, which isn’t always possible with CNC machining due to limitations in cutting tools such as end mills and drill bits (typically straight).
Is CNC Machining Better than 3D Printing?
CNC machining and 3D Printing have proven to be useful methods for creating custom components. They each have their strengths and weaknesses, but which is better?
In terms of cost, CNC machining is generally more expensive than 3D Printing. This is because the raw materials used in CNC machining are more expensive than the plastic filament used in 3D Printing, which comes at a much lower cost per unit. The materials used in a CNC milling process also require much more setup time and specialized equipment.
CNC machining also has a higher accuracy rate than 3D Printing due to its ability to use multiple motion axes simultaneously. Rather than moving along one axis like a 2-axis mill or lathe, CNC machines can move in three dimensions simultaneously, so they don’t have to stop and reorient themselves whenever they need to move across an object’s surface. This allows them to cut incredibly complex shapes that would be impossible for a single-axis machine tool like a lathe or milling machine.
However, this isn’t always true of CNC mills like the Vectric Aspire that use 5-axis functionality. They can only do so much independently before requiring additional support from software programs like V electric Cut 2D.

A factory for all your manufacturing needs: ETCN
When it comes to manufacturing, there is nothing that can replace experience. Many businesses favor using third-party manufacturing services to ensure consistent and accurate results. Such services allow you to maintain the same quality of your products without spending an exuberant amount in capital investment. For the best CNC machining and 3D printing services, the most natural choice for your business is ETCN.