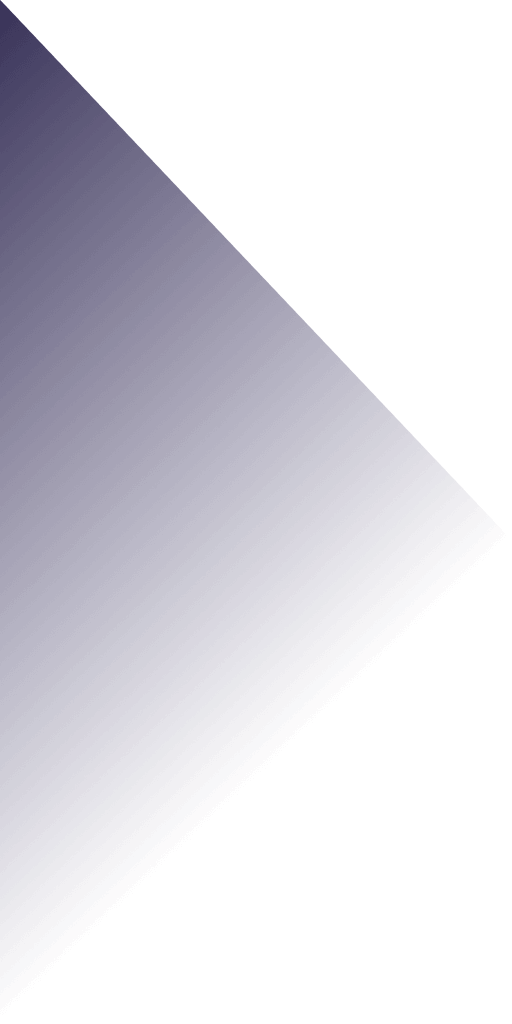
Teflon is a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) material. It is 3.5mm thick and 65mm DIA. This material is very thin and requires tight tolerances for the machine. It must also be clamped with very little air pressure to release easily.
Easy to machine
PTFE, or polytetrafluoroethylene, is a highly resistant thermoplastic that can be easily machined. Its properties make it suitable for various parts, including sliding elements, joints, bearings, and housings. Machined components made of PTFE may be a bit brittle, and tolerances may be difficult to achieve. Because of this, Teflon must be molded and finished using water-soluble, non-aromatic coolants.
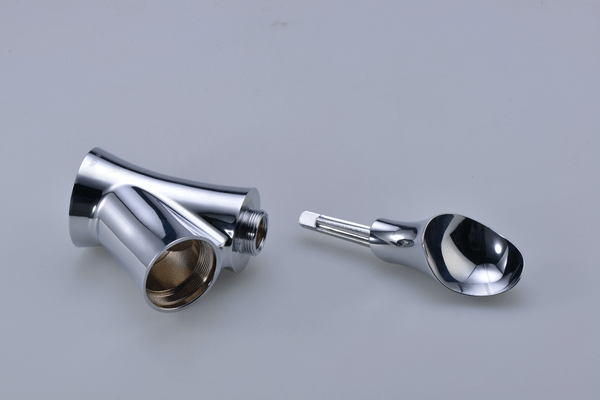
CNC machining is a common process for manufacturing Teflon parts. CNC machining is a good choice for machining this material, as it is soft, dense, and can be easily manipulated. Machining Teflon is highly reliable and efficient, but ensuring high precision can be challenging.
Using a CNC machining process, a reputable company will make the material as smooth and precise as possible. This technique will ensure that parts are not damaged and are not subject to dimensional changes even when subjected to corrosive environments. Additionally, the material is self-lubricating, so if it’s placed in a corrosive medium, it won’t change size.
PTFE, also known as Teflon, is a thermoplastic fluoropolymer made by the company COMCO Plastics. It is a soft material with low friction and high-temperature resistance. PTFE is hydrophobic and is resistant to acids, alkalis, and solvents. The material is also highly resistant to heat.
PTFE is widely used for low-friction parts and wire laying. Its high melting point makes it a good alternative to polyethylene and acetal and makes for an excellent insulator. It’s incredibly slippery, and its machining properties make it a perfect choice for sealing and insulating parts and in the electronics industry.
Has low friction
High-quality steel can be forged into high-quality components using low-friction materials. Several machining processes have been studied to determine which one is most effective. These techniques are abrasive jet machining (AJM) and milling machining (MM). AJM produces a surface with micro craters for oil storage, which reduces friction coefficients. On the other hand, MM produces tool marks, which can cause high friction coefficients.
The smallest grain size is one of the main factors affecting friction, and the ultrafine grain size is one of the most important. The ultrafine grain size makes it possible for the friction coefficient to be very low. In addition, this grain refinement increases the number of grain boundaries, which hinders the transmission of dislocations.
Low-friction plastics are ideal for many industrial applications. They are a great substitute for metal because of their wear resistance and durability. In addition, low-friction plastics are more resistant to external influences and less costly to produce. Furthermore, they keep moving parts clean and can reduce maintenance costs.
Generally, the friction coefficient of conventional metals is 0.1-0.3. This level of friction limits global sliding and inhibits reciprocating sliding. The initial friction coefficient also inhibits global sliding. Instead, partial slip occurs near the contact edges, stabilizing forces and reducing friction.
Low-friction coatings can also improve the productivity and efficiency of the machining process. A low-friction coating can increase tool life by up to 50 percent, resulting in significant savings. Low-friction coatings can also reduce the cost of tooling. If cutting the material is too hard for a standard coating, consider using a low-friction coating.
Is easier to machine than POM
While POM and Teflon have a similar chemical composition, they have several significant differences. The first is their high melting points. While POM is much stronger than Teflon, it is also less uniform cross-section, which means that not all geometries will stay stable during the machining process. While both materials have advantages, POM is better suited for larger quantities and mass production, while Teflon is better for high-quality surface finishes.
Teflon is a softer material than POM, making it easier to machine. It is also less brittle than POM, making it ideal for engineering-grade applications. However, Teflon has some disadvantages, including its prone to leave burrs, which may result in defects. However, these defects can easily be eliminated through standard surface finishing methods.
Teflon is more expensive than POM, but its machineability is better. It’s easier to cut and machine, making it a more suitable choice for high-volume production. While POM is more resistant to fuel and other chemicals, it’s not as easy to bond to metal.
Teflon has excellent chemical resistance, is a non-stick material, and is a popular choice for machined parts. It’s also suitable for a wide range of applications. Because of its low friction and low coefficient of friction, Teflon parts won’t change size even if exposed to corrosive media. CNC machining Teflon parts requires knowledge of the material and the skill to operate a CNC machine.
Regarding machineability, POM is a far better choice for most applications. Its low friction coefficient makes it an ideal choice for parts that require low temperatures and pressure. POM is easier to machine, so it’s a good choice for those looking for a high-quality product with great performance.
Is easier to machine than PTFE
While PTFE and Teflon are both excellent materials, there are some differences. For one, Teflon is easier to machine than PTFE. In addition, Teflon has a lower cost per part than PTFE. PTFE is often used in various industries and products, from the aerospace industry to the computer industry. Because of its lubricity, it is ideal for coating parts in many different ways. PTFE coatings can greatly increase the life of a part.
The machining process for PTFE parts is similar to that of other materials, although the material is more difficult for the machine if it has unbalanced elements. Another reason PTFE is difficult to machine is that the material cannot cool while turning. This means that parts with tight tolerances may need to be made from another material.
Another reason why Teflon is easier for the machine is its flexibility. It is easy to cut and shape by hand but has a high melting point. Because of this, PTFE is used in many products and applications, including wires, medical equipment, and cooking utensils. Additionally, it is chemically inert and insoluble in most solvents.
Using a water-soluble coolant will help the Teflon parts achieve the best surface finish and tolerances. It is also recommended that you use non-aromatic coolants for Teflon machining. A water-soluble coolant is also important because Teflon is soft and can leave marks on a machine.
Unlike PTFE, ePTFE is not very common in products. However, the ePTFE material is used to manufacture certain garments, such as GORE-TEX. The GORE-TEX brand carries considerable recognition worldwide. A GORE-TEX jacket can cost upwards of $70-$200.
Polytetrafluoroethylene, or PTFE, is a chemically inert thermoplastic that is ivory-white. Its non-stick properties make it an ideal material for non-stick cookware. PTFE coatings are also used in electrical components.